PhoneSat
NASA’s Smartphone Nanosatellite
Mission
PhoneSat is a nanosatellite, categorizing the mass as between one and ten kilograms. Additionally, PhoneSat is a 1U CubeSat, having a volume of around one liter. The PhoneSat Project strives to decrease the cost of satellites while not sacrificing performance. In an effort to achieve this goal, the project is based around Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) electronics to provide functionality for as many parts as possible while still creating a reliable satellite. Two copies of PhoneSat 1.0 (a and b) are being launched mid April 2013 along with an early prototype of PhoneSat 2.0 referred to as PhoneSat 2.0.beta.

Phonesat during a high altitude balloon experiment.
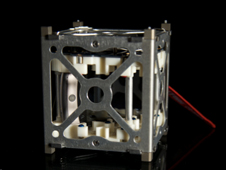
PhoneSat v2 is a technology demonstration mission intended to increase the functional capabilities of PhoneSat v1 and demonstrate complete satellite functionally in a low cost package. The satellite is built around the Nexus S smartphone which will be running the Android operating system and will be enclosed in a standard 1U cubesat structure. The main function of the phone is to act as the Onboard Computer, but the mission will also utilize the phone’s SD card for data storage, 5MP camera for Earth Observation, 3-axis gyroscope and 3-axis magnetometer for Attitude Determination, and 3-axis reaction wheel control system and 3-axis magnetorquer control system for Attitude Control.
 They are going to a very low orbit so they will only stay on orbit for about 10 days. The satellites are sending beacon data down using the radio amateur band frequency at 437.425MHz. The mission consists of taking some pictures of the Earth and sending them to ground in the form of small packets of data. Because it is a such a low orbit, we need to have as many radio ground stations around the world as possible in order to accomplish the mission.
They are going to a very low orbit so they will only stay on orbit for about 10 days. The satellites are sending beacon data down using the radio amateur band frequency at 437.425MHz. The mission consists of taking some pictures of the Earth and sending them to ground in the form of small packets of data. Because it is a such a low orbit, we need to have as many radio ground stations around the world as possible in order to accomplish the mission.
The main mission objective is to demonstrate each of the core subsystems: Attitude Determination, Attitude Control, Two-way communications and solar cell power generation.
- 1U standard cubesat structure provided by Pumpkin, inc.
- Size: 10x10x10 cm
- Weight: 1.3kg
- Antenna: quarter wave monopole tape measure antenna placed at the middle of one of the edges of the cube
Building the Phonesat Satellites:
Orbital parameters
Name PhoneSat NORAD 39144 COSPAR designation 2013-016-C Inclination (degree) 51.604 RAAN 280.443 Eccentricity 0.0014016 ARGP 40.232 Orbit per day 16.4813285 Period 1h 27m 20s (87.33 min) Semi-major axis 6.521 km Perigee x apogee 134 x 152 km Drag factor 0.000245410 Mean Anomaly 322.277
Downlink
437.425 MHz, FM, 1k2 AFSK AX.25
Call
GRAHAM (ID A) – KJ6KRW-2
BELL (ID B) – KJ6KRW-1
ALEXANDER – KJ6KRW
Status
Launch date: 2013/04/17, Orbit: 270km x 300km, inclination: 51.5deg. Launched on April 21, 2013 and active. Re-entered the Earth atmosphere. No longer active.
TLE
GRAHAM 1 39142U 13016A 13114.89139670 .02066248 11824-4 11888-2 0 125 2 39142 051.6312 294.1214 0011318 353.4416 006.6606 16.18063182 484 BELL 1 39143U 13016B 13114.89029360 .02779577 11872-4 14142-2 0 147 2 39143 051.6283 294.1154 0011084 343.5055 016.9415 16.19669199 498 ALEXANDER 1 39146U 13016E 13114.89004989 .02887841 11883-4 14290-2 0 38 2 39146 051.6237 294.1128 0010785 344.8223 015.2784 16.20034403 395
Received Telemetry
April 22, 2013 14:55 UTC
1:Fm KJ6KRW-2 To CQ Via TELEM [16:50:42R] ÿ5l^lb!<<*"#ljr270!;mec5[M!#!j?fKaNUs$Mh?5!tAfc+Y'2CHk0QjZ]>JW^-%R!5[KA!(%bmzzzzzzzz!,,q[Ci:G.Ec5e;FD,5.@<Q.%ÿ 1:Fm KJ6KRW-1 To CQ Via TCPIP [16:51:02R] ÿ63$uc!<<*"$NL/4h#IEZ8cShk!#!lWCHu[hpHt)gM*mD<g40/'!'`3ea1nNXl+tF@!5^2c!'tH%zzzzzzzz!,,q[Ci:G.Ec5e;FD,5.@<Q.%ÿ 1:Fm KJ6KRW To CQ Via TELEM [16:51:08R] charging814,0,0,0
Received telemetry pictures:


Telemetry
PhoneSat 1.0
Three different types of packets ASCII85 encoded. We are encoding bits instead of ASCII characters. Therefore, if you want to decode the packet, normal online ASCII85 decoders will not work. Use PhoneSat’s Decoder to decode your packets.
Health Data Packet
After being decoded, the packets will contain the following data:
ID: 1byte, identifier of which satellite you have received from. Restarts: number of restarts of the PhoneSat App. Reboots: number of reboots of the phone. Counter: number of packets sent since the beginning of the mission. Phase1: number of packets sent during phase 1 (only health data). Phase2: number of packets sent during phase 2 (health data and picture packets). Time: unix time in seconds. Voltage: battery Voltage in Volts. Temp1: exterior temperature in Kelvin. Temp2: interior temperature in Kelvin. Accel: accelerometer value for X, Y, Z axes from the phone sensor in m/sec2. Compass: magnetic field value for X, Y, Z axes from the phone sensor in nanoTesla. Text: “hello from the avcs”.
Safe Mode Packets
V: Last ten values of the Voltage prior to last reboot in Volts. OutT: Last ten values of the Exterior Temperature prior to last reboot in Kelvin. InT: Last ten values of the Interior Temperature prior to last reboot in Kelvin.
Picture Packets
These pictures can be converted into png pictures using Google’s webp converter. You will receive small parts of one big picture and once we have all the pieces, we will put it together and post it in our website!
PhoneSat-2
Sensors from the phone
Time: unix time time in milli seconds. Reboot: number of reboots of the phone. Counter: number of packets sent since the beginning of the mission. Packet type: for this packet will be sensors from the phone (1). Phase: phase in which the satellite is (we have 3 phases). Compass: magnetic field value for X, Y, Z axes from the phone sensor in nanoTesla. Gyro: spin rate for X, Y, Z axes from the phone sensor in deg/sec. Accel: accelerometer value of X, Y, Z axes from the phone sensor in m/sec2.
Current and voltage values
Time: unix time in milli seconds. Reboot: number of reboots of the phone. Counter: number of packets sent since the beginning of the mission. Packet type: for this packet will be current and voltage values (2). Phase: phase in which the satellite is (we have 3 phases). Voltage: battery voltage (digital value to be converted to Volts). Current: values from the boards (5 values) (digital value to be converted to mA) Current: values from the solar cells (6 values) (digital value to be converted to mA).
Temperatures
Time: unix time in milli seconds. Reboot: number of reboots of the phone. Counter: number of packets sent since the beginning of the mission. Packet type: for this packet will be current and voltage values (3). Phase: phase in which the satellite is (we have 3 phases). Temp: temperatures (11 values) (digital value to be converted to Kelvin).
BDot packet
Reboot: number of reboots of the phone. Counter: number of packets sent since the beginning of the mission. Packet type: for this packet will be current and voltage values (4). Phase: phase in which the satellite is (we have 3 phases). Gyro: five sets of gyroscope values in X,Y,Z axes in deg/sec (15 values in total)
Charging packet
Charge: charging message. Volt: battery voltage (digital value to be converted to Volts). Counter: counter.
Homepage and other references
PhoneSat webpage
NASA small satellites information
